The Dawn of Edge Computing: Revolutionizing Data Processing
As technology swiftly advances, edge computing has become a game-changing approach, revolutionizing the management and processing of data. While cloud computing has long been the foundation of data storage and processing, edge computing is now stepping into the spotlight by bringing these capabilities closer to the data source. This paradigm shift boosts efficiency, slashes latency, and opens up new horizons for businesses and consumers alike.
Understanding Edge Computing:
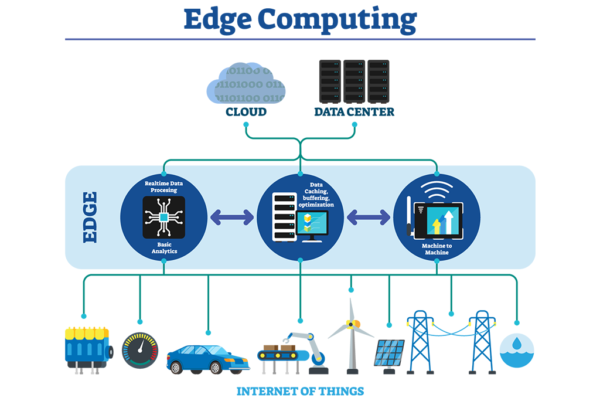
Edge computing processes data at or near its generation point, diverging from the traditional reliance on centralized cloud data centers. By decentralizing computation and storage, edge computing significantly shortens the distance data must travel, resulting in quicker processing times and lower bandwidth usage. This method is particularly beneficial for applications demanding real-time data processing and rapid response.
Why Edge Computing is Gaining Momentum:
Several critical factors are driving the rapid adoption of edge computing:
- Explosion of IoT Devices: With the surge in Internet of Things (IoT) devices, a vast amount of data is being generated at the network’s edge. Local data processing enables quicker responses and more efficient use of network resources.
- Demand for Low Latency: Applications like autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and industrial automation require immediate processing capabilities. Edge computing provides the low-latency environment essential for these technologies to operate effectively.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the volume of data transmitted to centralized data centers, easing network congestion and cutting operational costs.
- Enhanced Data Security and Privacy: Keeping data closer to its source reduces the risk of breaches during transmission, strengthening security and privacy measures.
Practical Applications of Edge Computing:
Edge computing is already transforming various industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Healthcare: In remote patient monitoring, edge devices process health data locally, delivering real-time alerts and minimizing the need for constant data transmission to central servers. This enhances patient care and optimizes healthcare resources.
- Retail: Smart stores using edge computing can analyze customer behavior in real-time, providing personalized experiences and optimizing inventory management, leading to improved customer satisfaction and increased sales.
- Manufacturing: In smart factories, edge computing enables predictive maintenance by analyzing data from machinery sensors on-site. This reduces downtime and boosts production efficiency.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles depend on edge computing to process data from sensors and cameras in real-time, facilitating split-second decision-making for safe and efficient operation.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its many advantages, edge computing also presents challenges that organizations must tackle:
- Infrastructure Management: Establishing and maintaining a distributed network of edge devices can be intricate and demanding in terms of resources.
- Interoperability: Ensuring seamless communication and compatibility between edge devices, cloud services, and legacy systems can be challenging. Standardization and interoperability are crucial for successful integration.
- Data Management: With data processed at multiple edge locations, organizations must develop effective data management strategies to ensure consistency, accuracy, and regulatory compliance.
The Future of Edge Computing:
The future of edge computing looks promising, with technological advancements continually enhancing its capabilities. The widespread adoption of 5G networks will further bolster edge computing by offering increased bandwidth and reduced latency. Additionally, innovations in artificial intelligence and machine learning at the edge will enable even more sophisticated and autonomous decision-making processes.
In conclusion, edge computing signifies a major shift in data handling and processing, providing significant benefits for latency-sensitive applications, bandwidth optimization, and data security. As industries increasingly embrace this technology, edge computing will play a vital role in our connected world, driving innovation and efficiency across various domains.
FAQs:
1. What is edge computing?
Edge computing involves processing data near its point of origin, instead of using centralized cloud servers. This approach reduces latency, improves efficiency, and conserves bandwidth by handling data closer to where it’s generated.
2. How is edge computing different from cloud computing? Cloud computing centralizes data processing in remote data centers, whereas edge computing decentralizes it, bringing computation and storage closer to the data source. This reduces the distance data must travel, offering faster response times and lower latency.
3. What are the key advantages of edge computing? The primary benefits include decreased latency, better bandwidth usage, enhanced data security and privacy, and the ability to process data in real-time, which is essential for applications like autonomous vehicles and smart manufacturing.
4. Where is edge computing being applied today? Edge computing is transforming various industries, including healthcare (real-time patient monitoring), retail (smart stores and inventory management), manufacturing (predictive maintenance in factories), and transportation (real-time processing for autonomous vehicles).
5. What challenges does edge computing present? Some of the main challenges include managing a complex and resource-intensive infrastructure, ensuring seamless interoperability between different systems and devices, and developing robust data management strategies to maintain data accuracy and compliance.
6. How does edge computing improve data security and privacy? By processing data locally rather than transmitting it to distant data centers, edge computing reduces the risk of data breaches during transmission. This local handling of data enhances overall security and privacy.
7. What role does edge computing play in the Internet of Things (IoT)? Edge computing is crucial for IoT, enabling real-time data processing and analysis at the network’s edge. This capability is essential for managing the large volumes of data generated by IoT devices, facilitating quicker responses and more efficient resource usage.
8. How will the advent of 5G impact edge computing? The widespread adoption of 5G networks will greatly enhance edge computing by providing higher bandwidth and lower latency. This will enable more advanced and responsive edge applications, further expanding its potential.
9. Can edge computing coexist with existing cloud infrastructure? Absolutely. Edge computing is designed to work alongside cloud computing. While edge computing addresses real-time processing and immediate data needs, cloud computing can handle long-term storage, in-depth data analysis, and broader data management tasks.
10. What future trends can we expect in edge computing? Looking ahead, advancements in AI and machine learning will likely drive more autonomous decision-making at the edge. Additionally, as 5G networks become more prevalent, edge computing will become faster and more efficient, spurring further innovation across various sectors.




