Closing the Digital Divide: Understanding the Gap and Its Consequences
The term “digital divide” describes the disparities in access to modern information and communication technologies between various individuals, households, and communities. As our reliance on digital platforms for essential services, education, and social interaction increases, it becomes vital to comprehend and address this divide.
What Constitutes the Digital Divide?
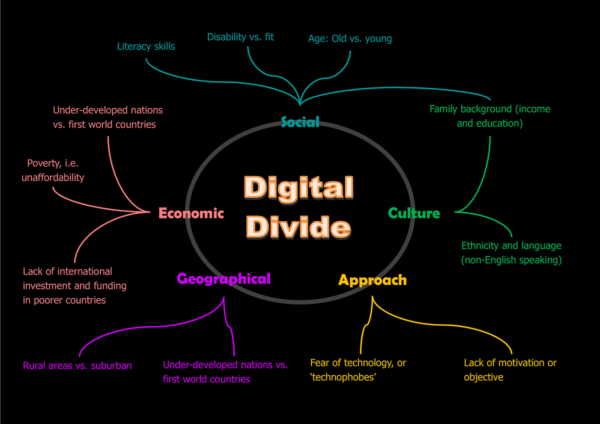
The digital divide encompasses more than just a lack of access to the internet or technology; it also includes the skills and knowledge needed to utilize these resources effectively. This gap can be observed through several lenses, including socioeconomic status, geographic location, age, and educational background.
Factors Contributing to the Digital Divide:
- Economic Barriers:
Cost remains a significant obstacle to technology access. For many low-income families, the expenses associated with internet service and devices are simply too high. As a result, while some enjoy the benefits of high-speed internet and advanced technology, others are left struggling to secure basic connectivity. - Geographic Limitations:
Rural areas and underserved urban regions often lack the necessary infrastructure for reliable internet connectivity. While metropolitan areas may boast multiple service providers and fast internet options, many rural communities find themselves with few or no choices. - Educational Disparities:
Skills and knowledge are critical in bridging the digital divide. Individuals who have not received sufficient education or training may find it challenging to use available technologies. This digital literacy gap can prevent full participation in the digital world, limiting personal and professional opportunities. - Age-Related Factors:
Age can significantly influence technology use. Older adults, for instance, may not feel as comfortable or familiar with digital tools compared to younger generations, leading to a generational technology gap.
Consequences of the Digital Divide:
The ramifications of the digital divide are extensive, impacting various facets of life:
- Access to Education:
In today’s learning environment, digital access is paramount. Students without reliable internet struggle to complete assignments, engage in online education, and access valuable resources, ultimately affecting their academic success and future prospects. - Economic Disparities:
The digital divide can worsen economic inequalities. Individuals without technological access may miss out on job openings, training opportunities, and remote work options, perpetuating a cycle of poverty that is hard to break. - Healthcare Disparities:
Telehealth has become essential, especially post-pandemic. Yet, those lacking access to technology may find it difficult to connect with healthcare providers or retrieve critical health information online, resulting in disparities in health outcomes. - Social Isolation:
A lack of connectivity can lead to social disconnection, particularly for seniors and those in remote areas. The internet facilitates communication and community interaction, and without it, individuals may feel increasingly isolated from society.

Strategies for Bridging the Digital Divide:
- Enhancing Infrastructure:
Expanding broadband networks in underserved areas is vital. Collaborative efforts between government and private sectors can help ensure that high-speed internet reaches all communities. - Making Access Affordable:
Initiatives that provide subsidized internet services and devices can help low-income families gain necessary access. Community Wi-Fi hotspots also offer essential connectivity to those in need. - Fostering Digital Literacy:
Educational initiatives focused on enhancing digital skills are crucial. Workshops, online courses, and community programs can equip individuals of all ages with the technology proficiency they need. - Promoting Inclusivity:
Technology developers and policymakers must emphasize inclusivity in their approaches. This involves creating accessible technology for people with disabilities and offering resources for non-native speakers and older adults.
Conclusion:
The digital divide is a multifaceted issue with far-reaching implications for individuals and society at large. Tackling this challenge demands a comprehensive strategy that includes infrastructure investment, affordable access, education, and a commitment to inclusivity. By bridging the digital divide, we can build a more equitable and interconnected society, ensuring that everyone has the opportunity to succeed in an increasingly digital landscape.
FAQs:
1. What does the term “digital divide” mean?
The digital divide refers to the disparity between individuals and communities who have access to digital technologies and the internet and those who lack that access. This gap can be influenced by factors such as income, geographic location, age, and educational background, impacting people’s ability to participate in the digital age.
2. What key elements contribute to the digital divide?
Several key factors contribute to the digital divide, including:
- Economic obstacles: The high cost of internet subscriptions and devices can prevent many from accessing necessary technology.
- Geographical challenges: Rural and low-income urban areas often lack the infrastructure needed for reliable internet service.
- Educational disparities: Limited digital literacy and training can make it difficult for individuals to effectively use technology.
- Age-related differences: Older adults may feel less comfortable navigating technology compared to younger generations.
3. How does the digital divide impact education?
Students without dependable internet access find it challenging to complete their assignments, participate in online classes, and utilize educational materials. This lack of access can negatively affect their academic achievements and future opportunities.
4. What implications does the digital divide have for the economy?
Those without technological access often miss out on job opportunities, training programs, and the potential for remote work, contributing to a cycle of economic inequality and limiting their upward mobility.
5. In what ways does the digital divide affect healthcare access?
With the increasing reliance on telehealth services, individuals without reliable internet may struggle to connect with healthcare providers or access critical health information, resulting in significant health disparities.
6. What strategies can help close the digital divide?
To effectively address the digital divide, a comprehensive approach is needed, which includes:
- Enhancing infrastructure to expand broadband access in underserved communities.
- Providing affordable internet options and devices to low-income households.
- Encouraging digital literacy through community education initiatives and training workshops.
- Promoting inclusive technology development to accommodate diverse user needs.
7. What initiatives exist to tackle the digital divide?
Various organizations and governments are actively working to bridge the digital divide through initiatives such as subsidized internet programs, expanding broadband networks in rural regions, and offering community-based digital training to improve tech skills.
8. How can individuals play a role in bridging the digital divide?
Individuals can contribute to closing the digital divide by advocating for equitable technology policies, volunteering with organizations that provide technology education, and supporting local initiatives focused on enhancing internet access.
9. Is the digital divide solely a concern for developing nations?
While the digital divide is frequently highlighted in developing countries, it remains a pressing issue in developed nations as well. Many rural and economically disadvantaged urban areas struggle with significant barriers to accessing technology, showcasing that the divide exists globally.
10. What future developments might impact the digital divide?
Advancements in technology, such as the rollout of 5G networks and satellite internet options, have the potential to narrow the digital divide by offering faster and more reliable connectivity in underserved regions. However, ongoing efforts are necessary to ensure equitable access to these emerging technologies.