Unveiling the Circular Economy: Paving the Way to Sustainable Tomorrow
In a world increasingly aware of its ecological footprint, the concept of a circular economy emerges as a beacon of innovation and sustainability. Unlike traditional linear models of production and consumption, which often lead to resource depletion and environmental degradation, the circular economy presents a transformative approach. It seeks to reimagine how we utilize resources, aiming not only to minimize waste but also to create a closed-loop system where materials and products are continually reused, recycled, or repurposed.
Embracing Circularity: What It Means
At its core, the circular economy challenges the status quo by advocating for a regenerative system that prioritizes resource efficiency and longevity. It encourages businesses and consumers alike to rethink how products are designed, manufactured, and consumed, emphasizing durability, repairability, and recyclability. By doing so, it aims to reduce the reliance on finite resources and mitigate environmental impact while fostering economic resilience.
Key Principles in Action:
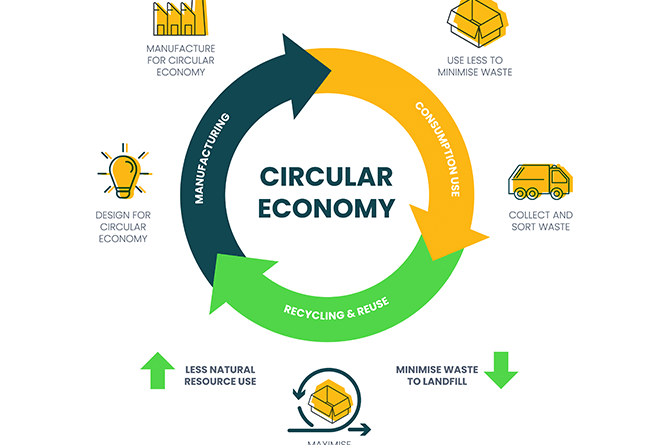
1. Designing for Longevity and Resource Efficiency
Central to the circular economy is the principle of designing products with longevity and resource efficiency in mind. This involves shifting away from the disposable culture towards products that are durable, easily repairable, and recyclable, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing waste.
2. Closing the Loop: Recycling and Upcycling
A cornerstone of the circular economy is the concept of closing material loops through effective recycling and upcycling processes. By transforming waste into new raw materials or products of higher value, businesses can minimize the extraction of virgin resources and reduce environmental impact.
3. Promoting Innovation and Collaboration
Embracing circularity encourages innovation across industries, from sustainable materials and production techniques to new business models that prioritize resource stewardship. Collaboration among stakeholders—businesses, governments, and consumers—is crucial in driving systemic change and overcoming challenges related to infrastructure, regulations, and consumer behavior.
Beyond Environmental Impact: Economic and Social Benefits
While environmental sustainability is a primary motivator, the circular economy offers numerous economic and social benefits:
- Cost Savings and Efficiency: Businesses can achieve cost savings through improved resource efficiency and reduced waste management expenses.
- Job Creation and Economic Resilience: The shift towards circular practices can stimulate job creation in sectors such as recycling, remanufacturing, and sustainable technologies, contributing to economic resilience and social well-being.

Challenges and Pathways Forward:
Transitioning to a circular economy is not without challenges, including technological barriers, policy gaps, and cultural shifts. Overcoming these hurdles requires collective action and commitment from stakeholders to invest in innovation, develop supportive policies, and raise awareness about the benefits of circular practices.
Embracing Circular Economy: Shaping a Sustainable Future
As global challenges such as climate change and resource scarcity intensify, the circular economy offers a transformative pathway towards sustainability. By rethinking how we produce, consume, and manage resources, we can create a more resilient and equitable future for generations to come.
In conclusion, embracing the circular economy is not just a choice but a necessity for safeguarding our planet and ensuring the well-being of future generations. Through collaborative efforts and innovative solutions, we can turn the vision of a circular economy into a reality, paving the way for a greener, more sustainable tomorrow.
FAQs:
1. What exactly is a circular economy?
A circular economy is a transformative approach to economic development designed to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a “take-make-dispose” model, a circular economy aims to keep products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible through strategies like recycling, reuse, and regeneration.
2. Why is the circular economy important today?
In today’s world, sustainability is paramount. The circular economy addresses critical environmental challenges by reducing resource consumption, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, and mitigating the impact of waste on ecosystems. Beyond environmental benefits, it also promotes economic growth through innovation and job creation in sustainable industries.
3. How does the circular economy differ from recycling?
While recycling is a key component of the circular economy, the concept extends far beyond simple waste management. Recycling involves converting waste materials into new products, whereas the circular economy encompasses a holistic approach. It focuses on designing products for longevity, optimizing resource use through efficient production processes, and fostering systems where materials are continually reused or repurposed.
4. What are the core principles guiding the circular economy?
The principles of the circular economy include:
- Design for Longevity and Durability: Creating products that are built to last and can be easily repaired or upgraded.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Establishing systems where materials and products circulate in closed loops, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Resource Efficiency: Maximizing the use of resources and minimizing waste through efficient production and consumption practices.
- Innovation and Collaboration: Encouraging innovation in product design, business models, and technologies, and fostering collaboration across industries and sectors.
5. How can businesses transition towards a circular economy?
Businesses can transition towards a circular economy by:
- Rethinking Product Design: Prioritizing sustainable materials, modular designs, and recyclability in product development.
- Adopting Circular Business Models: Implementing strategies such as product-as-a-service, where products are leased and returned for refurbishment or recycling.
- Engaging with Stakeholders: Collaborating with suppliers, customers, and policymakers to create a supportive ecosystem for circular practices.
6. What are the main challenges in implementing a circular economy?
Implementing a circular economy poses several challenges, including:
- Technological Innovation: Developing and scaling up technologies for efficient recycling and resource recovery.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing supportive policies and regulations that incentivize circular practices and address barriers to implementation.
- Consumer Behavior: Educating consumers and encouraging sustainable consumption habits.
- Investment and Financing: Securing funding and investment for circular initiatives and infrastructure development.
7. How can consumers contribute to the circular economy?
Consumers play a crucial role in advancing the circular economy by:
- Making Informed Choices: Opting for products that are durable, repairable, and recyclable.
- Practicing Sustainable Consumption: Reducing waste by repairing, reusing, and recycling products.
- Advocating for Change: Supporting businesses and policies that prioritize sustainability and circularity.
8. How does the circular economy support climate action?
The circular economy contributes to climate action by:
- Reducing Resource Extraction: Minimizing the extraction of virgin materials and reducing the associated greenhouse gas emissions.
- Lowering Waste Generation: Minimizing landfill waste and incineration, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Promoting Renewable Energy: Supporting renewable energy sources and sustainable practices within production and consumption cycles.
9. What are some successful examples of circular economy initiatives?
Successful examples of circular economy initiatives include:
- Textile Recycling Programs: Where used clothing is collected, sorted, and recycled into new textiles or materials.
- Closed-Loop Packaging Systems: Where packaging materials are designed for reuse or recycling, reducing plastic waste.
- Sharing Platforms: Such as ride-sharing and peer-to-peer rental services, which maximize the use of existing resources.
10. How can governments facilitate the transition to a circular economy?
Governments can facilitate the transition to a circular economy by:
- Developing Supportive Policies: Implementing regulations and incentives that encourage sustainable practices and circular business models.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Supporting the development of recycling facilities, renewable energy projects, and sustainable technologies.
- Promoting Education and Awareness: Educating businesses, consumers, and communities about the benefits and importance of the circular economy.